Kmesh Documentation
record of kmesh project
Kmesh 问题记录
本文主要记录个人在进行 Kmesh 开发过程中遇到的问题和解决方法。 主要是记录一下个人在开发过程中解决了哪些问题。
问题
问题 1,flaky test
这个问题是我首先在对 kmeshctl dump 命令增加按 name 排序的时候遇到的。
在第一次提交 PR 提交后,在 go test 的过程中出现了测试用例不通过的情况,但是明显有关代码并没有被修改。 通过简单的分析可以发现,失败的几个测试用例都是和证书相关的测试用例。显然是证书申请、轮转的时间超时了。因为测试用例中通过 time.Sleep 来等待,解决方法是通过延长时间和 request timeout 来解决,通过每隔 100ms 检查一次,最长等待 6s。 这种按时查询的方法挺常见的,k8s 和 istio 中提供相关的工具函数。
--- FAIL: TestSecurity (2.42s)
--- PASS: TestSecurity/TestBaseCert (0.31s)
--- FAIL: TestSecurity/TestCertRotate (2.11s)
panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference [recovered]
panic: runtime error: invalid memory address or nil pointer dereference
[signal SIGSEGV: segmentation violation code=0x1 addr=0x0 pc=0x128a169]
问题 2, IPsec 单元测试编写
这里主要是如何编写单元测试,涉及 ipsec handler 和 ipsec controller 的测试。这里先是让 Claude 帮忙生成了一些测试代码,然后再进行修改。编写的过程中需要学习 gomonkey, k8s fake 等库的使用。以及 k8s 中 secret 的使用,如何自定义 resource,自定义 controller 等。
在这个过程中也解决了一些小问题:
- 创建 ipsec controller 创建时需要读取 secret 中的内容,但是如果 secret 不存在会报错,因此需要先创建 secret,然后再创建 controller。这里新增了一个对文件不存在的处理。
func NewIPsecController(k8sClientSet kubernetes.Interface, kniMap *ebpf.Map, decryptProg *ebpf.Program) (*IPSecController, error) {
...
// load ipsec info
if _, err := os.Stat(IpSecKeyFile); err == nil {
err = ipsecController.ipsecHandler.LoadIPSecKeyFromFile(IpSecKeyFile)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to load ipsec key from file %s: %v", IpSecKeyFile, err)
}
} else if !os.IsNotExist(err) {
log.Errorf("failed to stat ipsec key file %s: %v", IpSecKeyFile, err)
}
...
}
- 在配置 IPsec state 和 policy 的时候,需要获取节点信息,如果失败需要有重试机制。这里重试机制失败。由于使用TypedRateLimitingQueue,调用 forget 方法会清除掉失败次数,这里错误的总是调用 forget 方法,导致重试机制失效。
func (c *IPSecController) processNextItem() bool {
...
if err := c.handleOneNodeInfo(node); err != nil {
if c.queue.NumRequeues(key) < MaxRetries {
log.Errorf("failed to handle other node %s err: %v, will retry", name, err)
c.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
} else {
log.Errorf("failed to handle other node %s err: %v, giving up", name, err)
c.queue.Forget(key)
}
+ return true // 这里新增
}
...
TypedRateLimitingQueue
A TypedRateLimitingQueue is an enhanced version of Kubernetes work queues that:
Provides type safety through Go generics (hence “Typed”) Implements rate limiting to control how fast items are processed Prevents duplicate items in the queue Handles retries with exponential backoff
需要阅读源码,理解其工作原理。实际上,ratelimiter会设置一个basedelay和maxdelay,并且记录失败次数,根据失败次数调整延迟时间,比如根据失败次数增加 2^failures ns。
-
Get: 获取一个item
-
Done: 标记一个item处理完成,出队列。我的理解是在 Get 到 Done 之间如果这个key重新被尝试加入了队列,那么会被标记为脏数据,重新加入队列
-
Forget: 标记一个item不再需要处理, 这个方法会清除该item的所有状态信息,包括失败次数。
type TypedRateLimiter[T comparable] interface {
// When gets an item and gets to decide how long that item should wait
When(item T) time.Duration
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for failing
// or for success, we'll stop tracking it
Forget(item T)
// NumRequeues returns back how many failures the item has had
NumRequeues(item T) int
}
问题 3,kmeshctl secret 命令
最开始 kmeshctl secret 命令需要手动创建一个 128 字符的十六进制字符串作为密钥,然后通过 kmeshctl secret --key=xxxx 来创建 secret。这样比较繁琐,因此增加了自动生成密钥的功能。
kmeshctl secret --key=$(echo -n "{36-character user-defined key here}" | xxd -p -c 64)
kmeshctl secret --key=$(dd if=/dev/urandom count=36 bs=1 2>/dev/null | xxd -p -c 64)
修改为对 secret 生命周期的管理,支持创建、查看、删除 secret。
# Create IPsec secret with random key
kmeshctl secret create
# Create IPsec secret with custom key
kmeshctl secret create --key=$(echo -n "{36-character user-defined key here}" | xxd -p -c 64)
# Get current IPsec configuration
kmeshctl secret get
# Delete IPsec secret
kmeshctl secret delete
问题 4, IPsec 启用后导致通信异常
之前 IPsec 启用后,如果未被 kmesh 管理的 pod 访问另一个节点上的 pod 会出现通信异常,表现为请求超时。 并且在 Kmesh 的日志中会看到如下错误:
time="2025-08-12T11:00:52Z" level=error msg="grpc reconnect failed, create workload stream failed, DeltaAggregatedResources failed, rpc error: code = Unavailable desc = connection error: desc = \"transport: Error while dialing: dial tcp 10.96.95.184:15012: i/o timeout\"" subsys=controller
或
2025-08-12T10:52:18.598907Z error cache resource:default failed to sign: create certificate: rpc error: code = Unavailable desc = connection error: desc = "transport: Error while dialing: dial tcp: lookup istiod.istio-system.svc: i/o timeout"
之后通过更加详细的测试确定了,下述情况会报错。
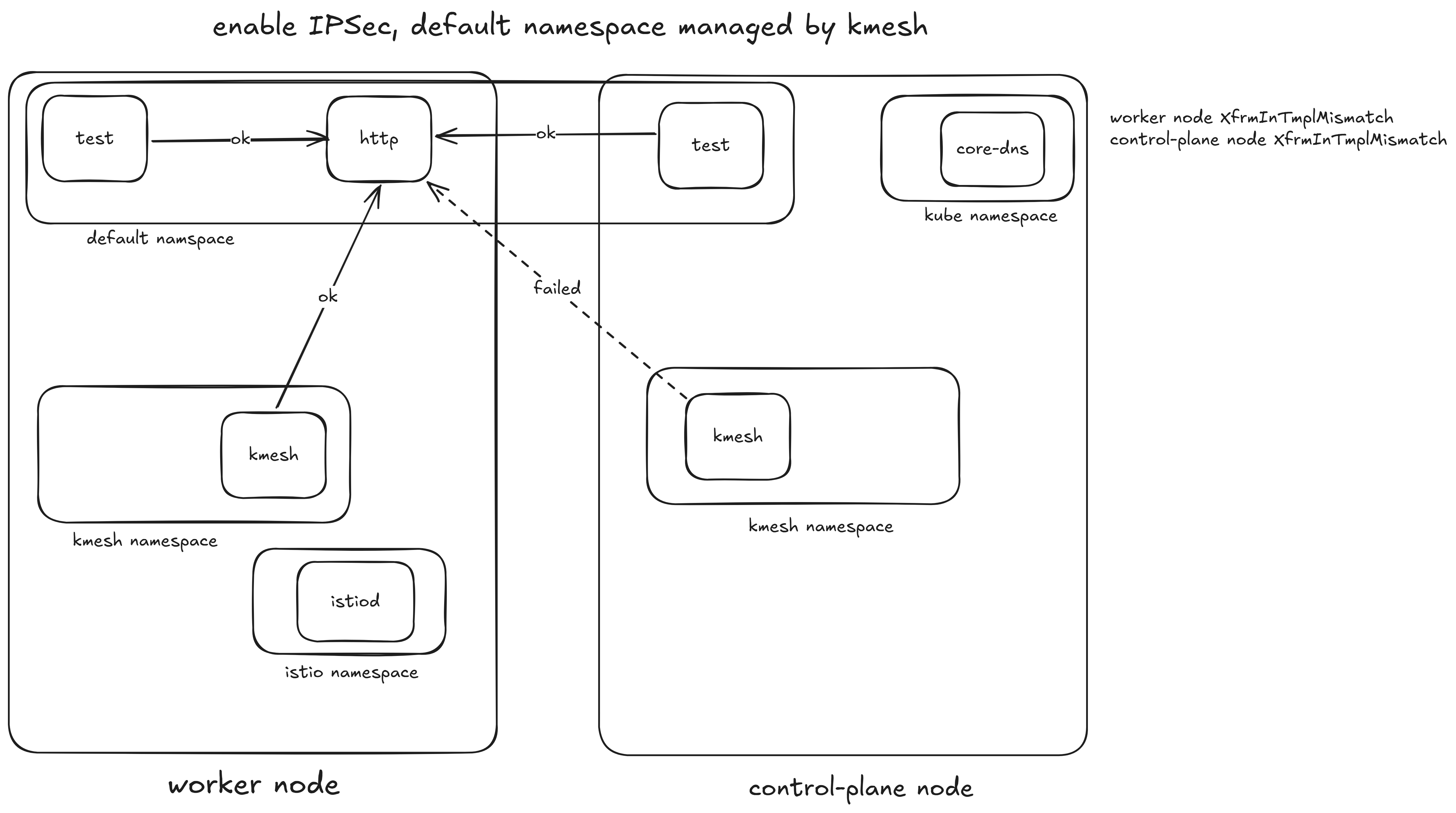
原因分析
- 现在的ipsec配置会把node上所有的的pod都纳入xfrm policy规则中,而不是只有被纳管的namespace中的pod。 这会导致,如istiod发送回的数据包由于没有挂载加密程序所以没有被加密,而数据包来到local nic之后,会匹配到的xfrm policy中的规则,但是由于没有被加密,内核选择丢弃了这些数据。因此会出现超时错误。 可能的解决方法是,调整xfrm policy的范围,使其只包含被kmesh纳管的pod的ip地址。
- 在node上cat /proc/net/xfrm_stat,发现很多的XfrmInTmplMismatch
- 不同node上的pod ip地址会有重叠吗?这个应该是不会的,具体还是要进一步了解有关实现。
问题的关键在于XfrmInTmplMismatch到底是因为什么原因导致的。在这个过程中考虑使用 kprobe 来进行跟踪,但是对 kprobe 缺乏了解,因此没有进行下去。因此,转而通过阅读内核代码来进行分析。
解决方法
- 找到内核中 XfrmInTmplMismatch 增加的位置。通过 AI 工具,找到了具体的位置在
__xfrm_policy_check函数中,且XfrmInTmplMismatch 的增加只在这个函数中出现。 - 阅读
__xfrm_policy_check函数的代码,发现首先会找到对应的 xfrm policy,如果匹配到了那么就会进一步检查sec_path,如果sec_path存在问题就会增加 XfrmInTmplMismatch 计数。这里具体来说,因为未被Kmesh纳管的pod发送过来的数据包没有被加密,因此 sec_path 为空,因此会增加 XfrmInTmplMismatch 计数。
内核源码位置
见地址
// net/xfrm/xfrm_policy.c
int __xfrm_policy_check(struct sock *sk, int dir, struct sk_buff *skb,
unsigned short family)
{
// 在前面这部分会检查是否有匹配的 xfrm policy
// 省略若干代码
// ...
// 如果policy策略是XFRM_POLICY_ALLOW,那么进一步检查sec_path
if (xp->action == XFRM_POLICY_ALLOW) {
// ... 省略若干代码
for (i = xfrm_nr-1, k = 0; i >= 0; i--) {
k = xfrm_policy_ok(tpp[i], sp, k, family, if_id); // 这里会返回-1
if (k < 0) {
if (k < -1)
/* "-2 - errored_index" returned */
xerr_idx = -(2+k);
XFRM_INC_STATS(net, LINUX_MIB_XFRMINTMPLMISMATCH); // 这里会增加 XfrmInTmplMismatch 计数,解释了我们观察到的现象
goto reject;
}
}
if (secpath_has_nontransport(sp, k, &xerr_idx)) {
XFRM_INC_STATS(net, LINUX_MIB_XFRMINTMPLMISMATCH);
goto reject;
}
// ... 省略若干代码
}
// ... 省略若干代码
}
匹配到policy之后会进一步检查sec_path,如果sec_path有问题就会增加 XfrmInTmplMismatch 计数。具体会通过 xfrm_policy_ok 来进行检查,sec_path 则被保存在sk_buff的extension中。通过skb_sec_path来获取。
static inline struct sec_path *skb_sec_path(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
return skb_ext_find(skb, SKB_EXT_SEC_PATH);
#else
return NULL;
#endif
}
static inline void *skb_ext_find(const struct sk_buff *skb, enum skb_ext_id id)
{
if (skb_ext_exist(skb, id)) { // 显然如果数据包没有经过xfrm处理,那么sec_path是不存在的, 返回空指针
struct skb_ext *ext = skb->extensions;
return (void *)ext + (ext->offset[id] << 3);
}
return NULL;
}
static inline bool skb_ext_exist(const struct sk_buff *skb, enum skb_ext_id id)
{
return skb->active_extensions & (1 << id);
}
static inline int
xfrm_policy_ok(const struct xfrm_tmpl *tmpl, const struct sec_path *sp, int start,
unsigned short family, u32 if_id)
{
int idx = start;
if (tmpl->optional) {
if (tmpl->mode == XFRM_MODE_TRANSPORT)
return start;
} else
start = -1;
for (; idx < sp->len; idx++) { // 已知 sec_path 为空,因此不会进入循环体,直接返回start,默认值为-1,因为我们在配置xfrm policy的时候tmpl->optional为false
if (xfrm_state_ok(tmpl, sp->xvec[idx], family, if_id))
return ++idx;
if (sp->xvec[idx]->props.mode != XFRM_MODE_TRANSPORT) {
if (idx < sp->verified_cnt) {
/* Secpath entry previously verified, consider optional and
* continue searching
*/
continue;
}
if (start == -1)
start = -2-idx;
break;
}
}
return start;
}
问题的原因找到了,但是还是没有办法进一步解决问题。这里进一步考虑为什么匹配到了 xfrm policy。
因为tc_decrypt 程序会对所有在 node 上的 pod ip 进行标记,因此所有发往 node 上 pod 的数据包都会被标记为 0x00d0,从而到达 xfrm in policy lookup 的时候会匹配到 xfrm policy,从而进一步检查 sec_path,导致 XfrmInTmplMismatch 增加。
因此首先的解决方法是调整 tc_decrypt 程序,使其只对经过加密的数据包进行标记。
在我们的实现中,需要明确一个在 node 网卡的 ingress 阶段的数据包,其是被加密的数据包还是未被加密的数据包。如果是加密的数据包,那么就需要进行解密处理;如果是未被加密的数据包,那么还需要进一步判断这个数据包是解密之后重新进入 ingress 的数据包,还是未被加密的 pod 发送过来的数据包。如果是解密之后重新进入 ingress 的数据包,那么就不需要进行任何处理;如果是未被加密的 pod 发送过来的数据包,那么就将这个数据包标记为不需要加密。
此外,如果是解密的数据包,我们通过设置 xfrm state output-mark 来标记这个数据包已经被解密过了,这样在 ingress 阶段就可以直接判断这个数据包是解密过的,从而不进行任何处理。并且确保 output-mark 的值和 xfrm policy 中的 mark 值保持一致。
所以,需要注意数据包的 mark 不能够出现冲突,否则会导致数据包被错误的处理。
// run at node nic and mark traffic need to decryption
SEC("tc_ingress")
int tc_mark_decrypt(struct __sk_buff *ctx)
{
struct nodeinfo *nodeinfo;
struct tc_info info = {0};
__u8 protocol = 0;
bool decrypted = false;
__u32 mark = 0;
if (parser_tc_info(ctx, &info)) {
return TC_ACT_OK;
}
if (is_ipv4(&info)) {
protocol = info.iph->protocol;
} else if (is_ipv6(&info)) {
protocol = info.ip6h->nexthdr;
} else {
return TC_ACT_OK;
}
if (protocol == IPPROTO_ESP) {
return TC_ACT_OK;
}
mark = ctx->mark;
decrypted = (mark == IPSEC_DECRYPTED_MARK); // IPSEC_DECRYPTED_MARK is same with xfmr state output-mark, which means
// packet was decrypted and then back to ingress
if (decrypted) {
return TC_ACT_OK;
}
ctx->mark = 0;
return TC_ACT_OK;
}
char _license[] SEC("license") = "Dual BSD/GPL";
int _version SEC("version") = 1;
其他
其他就是一些文档相关的内容,如网站上的文档、通过Kmesh捐赠到CNCF等。